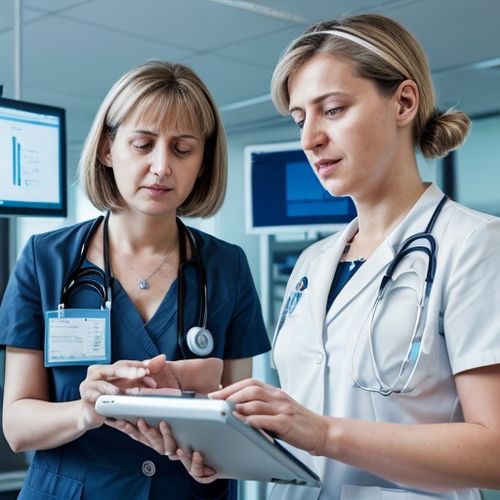
Germany has emerged as a European leader in integrating artificial intelligence diagnostic tools within primary care settings. The country's methodical approach combines technological innovation with rigorous healthcare standards, creating a framework for AI adoption that maintains patient safety while enhancing diagnostic accuracy.
Regulatory Framework
The German healthcare system has established clear guidelines governing AI implementation in clinical practice. These regulations address data privacy concerns, algorithm transparency requirements, and physician oversight protocols. Certification processes ensure only validated systems enter clinical workflows, with continuous monitoring of real-world performance.
System Capabilities
AI diagnostic platforms deployed in German primary care settings typically offer multi-modal analysis capabilities. These systems process symptoms, medical history, and basic test results to generate differential diagnoses. Some advanced platforms incorporate imaging analysis for common conditions, while others specialize in chronic disease management support.
Clinical Integration
German primary care practices have adopted a phased implementation model for AI tools. Initial applications focus on decision support rather than autonomous diagnosis, maintaining physician oversight. The technology integrates with existing electronic health record systems, minimizing workflow disruptions. Training programs ensure practitioners understand system limitations and appropriate use cases.
Performance Metrics
Early data indicates AI systems improve diagnostic accuracy for certain common conditions, particularly those with complex symptom presentations. The technology demonstrates particular value in flagging potential rare diagnoses that might otherwise be overlooked. Processing speed advantages enable more comprehensive evaluations during standard consultation windows.
Patient Acceptance
German healthcare providers report generally positive patient reception to AI-assisted diagnostics when properly introduced. Clear communication about the physician's ongoing oversight role appears crucial for maintaining trust. Privacy safeguards and transparency about data usage help address initial patient concerns.
Operational Impact
AI implementation affects practice operations in multiple dimensions. While reducing some administrative burdens, the technology creates new quality control requirements. Workflow analyses show net time savings for certain diagnostic processes, though initial learning curves can temporarily reduce efficiency.
Cost Considerations
The German reimbursement system has begun adapting to accommodate AI-assisted diagnostics. Current models typically bundle AI costs within existing consultation fees rather than creating separate billing items. Health economists debate long-term cost-effectiveness as the technology evolves.
Quality Assurance
Continuous monitoring systems track diagnostic outcomes and physician satisfaction. Regular algorithm updates incorporate new medical knowledge and address identified limitations. Peer review mechanisms ensure consistent performance across different practice settings.
Future Development
Next-generation systems aim to incorporate more comprehensive patient data, including genomic information and lifestyle factors. Researchers are exploring predictive capabilities for disease progression and treatment response. Integration with telemedicine platforms may expand access in underserved regions.
Challenges
Implementation hurdles include varying digital infrastructure across practices and the need for ongoing staff training. Some physicians report discomfort with changing diagnostic workflows. Ensuring equitable access across different practice types remains an ongoing consideration.
Germany's experience demonstrates both the potential and complexities of implementing AI diagnostics in primary care. The country's structured approach balances innovation with patient safety, creating a model for gradual, evidence-based adoption. As the technology matures, German primary care continues refining the optimal human-AI collaboration model to enhance diagnostic quality while preserving the physician-patient relationship.

By Emily Johnson/Mar 29, 2025

By Olivia Reed/Mar 29, 2025

By Benjamin Evans/Mar 29, 2025

By Jessica Lee/Mar 29, 2025

By Benjamin Evans/Mar 29, 2025

By Noah Bell/Mar 29, 2025

By Emily Johnson/Mar 29, 2025

By Grace Cox/Mar 29, 2025

By Megan Clark/Mar 29, 2025

By Sophia Lewis/Mar 29, 2025

By Joshua Howard/Mar 29, 2025

By Ryan Martin/Mar 29, 2025
By John Smith/Mar 29, 2025

By Megan Clark/Mar 29, 2025

By George Bailey/Mar 29, 2025

By Ryan Martin/Mar 29, 2025

By Benjamin Evans/Mar 29, 2025

By Emma Thompson/Mar 29, 2025

By Lily Simpson/Mar 29, 2025

By Amanda Phillips/Mar 29, 2025