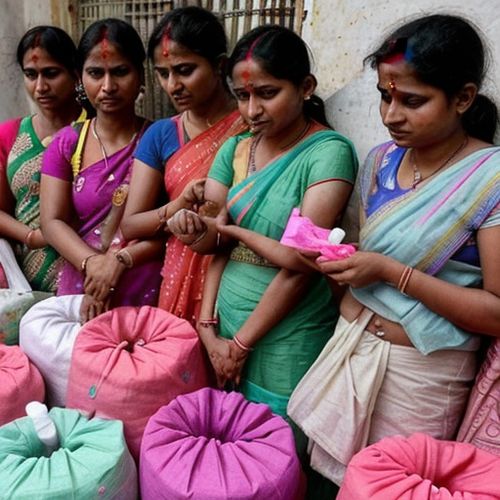
India's landmark decision to eliminate taxation on sanitary products represents a significant public health intervention aimed at improving menstrual hygiene management. The 2018 policy shift removed the controversial 12% Goods and Services Tax (GST) on sanitary pads and tampons, addressing both economic and gender equity concerns in menstrual health access.
Policy Framework
The tax exemption applies to all commercially manufactured disposable menstrual products meeting specified quality standards. The policy complements existing government programs distributing free products through schools and health centers. Regulatory provisions ensure pricing transparency and prevent manufacturers from absorbing the tax benefit as additional profit.
Market Response
Analysis indicates a 15-20% reduction in retail prices across major brands following implementation. Smaller regional manufacturers have entered the market, increasing product variety and local availability. Distribution networks have expanded to tier-2 and tier-3 cities, though rural penetration remains inconsistent.
Consumption Patterns
Sales data demonstrates steady growth in commercial product uptake, particularly among urban lower-middle class populations. The policy appears to have accelerated the shift from traditional alternatives to standardized hygiene products. Consumption increases correlate most strongly in the 15-24 age demographic.
Health Outcomes
Early indicators suggest reduced incidence of reproductive tract infections in monitored districts. School attendance data shows modest improvements in menstrual-related absenteeism, though other socioeconomic factors complicate attribution. Public health campaigns have leveraged the policy to amplify hygiene education efforts.
Equity Considerations
The exemption disproportionately benefits formal sector workers and students with disposable income. Challenges persist in reaching economically vulnerable groups who face accessibility rather than affordability barriers. The policy's urban bias reflects broader disparities in menstrual health infrastructure.
Manufacturing Impact
Domestic production capacity has expanded with increased investment in manufacturing facilities. The tax structure creates preferential conditions for local producers over imports. Quality control mechanisms have been strengthened to prevent substandard product proliferation.
Implementation Challenges
Enforcement difficulties emerge in monitoring price compliance at retail levels. Informal sector workers lack mechanisms to benefit from the policy. Geographical disparities in product availability persist despite price reductions.
Complementary Initiatives
The tax exemption operates alongside several government programs:
Behavioral Factors
Research indicates the policy has contributed to reduced stigma surrounding menstrual product purchase. Male family members demonstrate increased willingness to procure commercial products. The symbolic value of the tax removal appears to have exceeded its direct economic impact.
Environmental Considerations
The policy has inadvertently boosted disposable product consumption, raising concerns about sustainable alternatives. Recent amendments have extended tax benefits to emerging eco-friendly products to encourage market development.
Monitoring Mechanisms
The government has established tracking systems to assess:
Future Policy Directions
Potential expansions under consideration include:
India's menstrual product tax exemption represents an innovative fiscal approach to addressing gender health disparities. While demonstrating measurable impact on product accessibility, the policy's full potential requires complementary investments in education and infrastructure. The experience offers valuable lessons for other developing nations considering similar interventions to improve menstrual health management. Ongoing evaluation will determine the policy's long-term effectiveness in achieving comprehensive menstrual equity.

By Emily Johnson/Mar 29, 2025

By Olivia Reed/Mar 29, 2025

By Benjamin Evans/Mar 29, 2025

By Jessica Lee/Mar 29, 2025

By Benjamin Evans/Mar 29, 2025

By Noah Bell/Mar 29, 2025

By Emily Johnson/Mar 29, 2025

By Grace Cox/Mar 29, 2025

By Megan Clark/Mar 29, 2025

By Sophia Lewis/Mar 29, 2025

By Joshua Howard/Mar 29, 2025

By Ryan Martin/Mar 29, 2025
By John Smith/Mar 29, 2025

By Megan Clark/Mar 29, 2025

By George Bailey/Mar 29, 2025

By Ryan Martin/Mar 29, 2025

By Benjamin Evans/Mar 29, 2025

By Emma Thompson/Mar 29, 2025

By Lily Simpson/Mar 29, 2025

By Amanda Phillips/Mar 29, 2025